Boilers: What Are They & How Do They Work?
What is a boiler, and how does it work?
A heating boiler, in simple terms, is a metal chamber with a heating element. The boiler heats water to a temperature greater than that of the environment around it, then moves that heated water to radiators around the house. Boilers help to heat a home or commercial building steadily and evenly.
The exact structure of a boiler depends on the type you’re using. Many boilers have a large chamber, or tank, to hold heated water until it’s needed. Advances in heating technology have allowed for tankless water heaters to provide hot water on demand, but traditional water boilers still have a purpose in residential and commercial applications.
Let’s look more closely at how water boilers work to heat not only water but the home or commercial building at large.
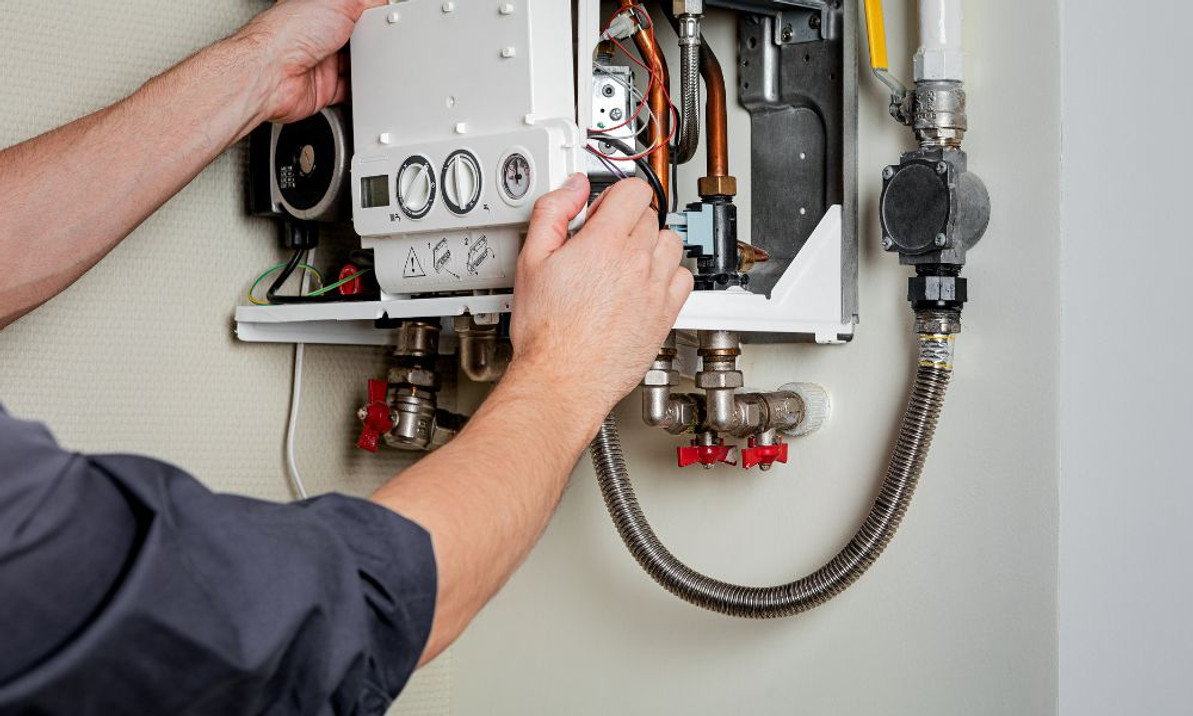
The Basic Anatomy of a Boiler
There is a wide variety of boilers available for purchase, and each will differ slightly in construction. However, each boiler has the same basic set of components that allows the system to heat water quickly and efficiently.
Burner
The burner is just what it sounds like: the component that combines air and fuel to create optimal combustion conditions for burning that fuel. Depending on the type of fuel your boiler uses, the burner will operate a little differently.
- Gas boilers utilize either an electric start or a pilot light to ignite natural gas and oxygen. This process occurs inside the combustion chamber, which we’ll discuss in greater depth later. Gas boilers are the most common boiler variety on the market as they’re relatively inexpensive to install and run.
- Oil boilers use fuel oil, which heats up and burns inside the combustion chamber to provide heat for the water. Oil boilers require an oil storage tank to hold that valuable fuel until it’s needed.
- Electric boilers burn more cleanly, using the burner to apply heat to the heating elements with electrical power. Heat is transferred more directly to the water instead of heating up fuel sources that combust.
Combustion Chamber
The combustion chamber combines three essential elements—fuel, oxygen, and heat—in tightly controlled amounts to create a chemical reaction. This element of your hot water boiler is commonly called the furnace.
Once the combustion process starts inside the chamber, it tends to sustain itself going forward. Heat is transferred through the walls of the combustion chamber to other boiler components via radiation.
Heat Exchanger
The reaction that occurs inside the combustion chamber produces heat as a by-product. This extra heat moves into the exchanger and heats water and other components via convection and conduction. There are a couple of varieties of heat exchangers commonly used in water boilers.
- Water-tube boilers move the water to be heated through a series of pipes, or tubes, with the heated gases moving along the outside of those tubes.
- Fire-tube boilers utilize much larger pipes inside a large drum. The gases heated from combustion pass through those tubes and heat the water inside the drum.
- Cast-iron sectional boilers use a variety of components made of cast iron, which is a highly effective heat conductor. The combustion chamber is surrounded by water and gas channels, and the heated gas heats the water within the channels.
How the Heating Process Works
While the specifics of the heating process will differ based on the fuel type and the configuration of the boiler, they each follow a similar series of steps.
- Step One: Water is heated inside the combustion chamber and begins to move through the pipes.
- Step Two: That hot water—or steam, depending on the boiler type—moves through pipes to radiator circuits located around the home or commercial building.
- Step Three: Hot water or steam moves across the walls of the radiator tubes, delivering heat to the rooms where those radiators are located.
- Step Four: After the hot water or steam has heated the radiators, it moves through the pipes back to the boiler in order to start the process anew. If the boiler uses steam to heat the radiators, this is the point where that steam cools down enough to become water again.
- Step Five: Return to Step One.
Other Types of Boilers
Many traditional boilers are only used to heat the air in the homes or commercial buildings where they’re installed. However, there are also boilers on the market that work as hot water heaters.
Tankless Coil Systems
Tankless heaters provide hot water on demand to your faucets; there’s no large chamber where the hot water sits until you’re ready to use it. Instead, when you turn on the hot water in your faucet, water runs over the boiler system’s heat exchanger right before flowing out of your faucet.
This method of heating water is particularly efficient in the winter months. Your boiler is already working to heat the air in your home, and the tankless system piggybacks off that extra heat to give you hot water. In the summer months, though, tankless water heating can make your energy bill higher.
Indirect Systems
An indirect hot water heater works similarly to a tankless system—but with a storage tank. Water runs over the heat exchanger and is stored in a tank separate from the rest of the boiler. When you turn on the hot water in your faucet or shower, the water moves from that storage tank to the faucet where you need it.
This form of heating is more consistently efficient than a tankless water heater. The boiler doesn’t need to turn on and off every single time you need hot water.
24hr Supply’s guide to what boilers are and how they work is a handy tool for remembering the basics of boiler systems. Each type of boiler has its own advantages, depending on the home or commercial building where it’s being installed.
From large commercial boilers to space-efficient tankless systems, 24hr Supply carries a wide variety of hot water boilers for a variety of applications. Contact us if you or your client have further questions about any of the boiler systems we offer.

Recent Posts
-
A Quick Guide To Understanding HVAC Load Calculations
There’s a science behind creating a space that’s both comfortable and energy-efficient. …Jul 17th 2025 -
7 Signs That Your Water Heater Is Leaking
A water heater might not be the flashiest appliance in your home, but when it starts acting up, it c …Jun 27th 2025 -
The Impact of Booster Pumps on Water Quality
Imagine turning on your faucet, only to watch a weak stream of water struggle its way out. It’ …Jun 16th 2025