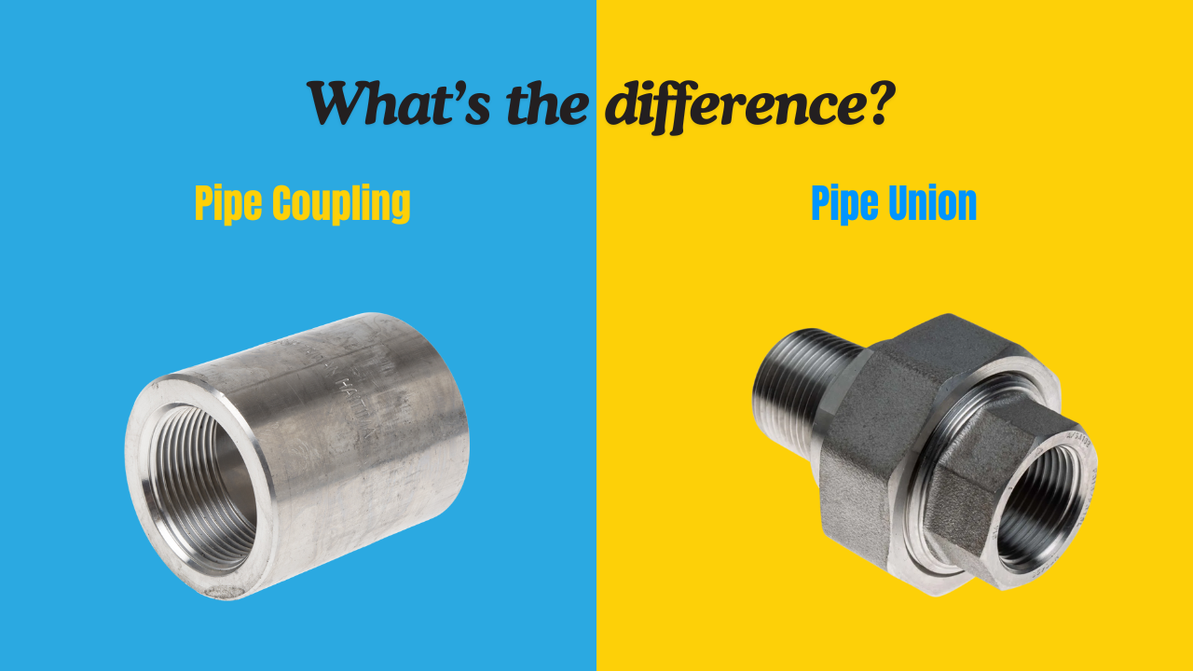
Coupling vs Union: What's the Difference?
Couplings and unions may look similar, but they serve different purposes. A coupling creates a permanent connection between two pipes, while a union provides a serviceable connection that can be disconnected without cutting or rotating the pipe.
Dive in to explore the key differences between couplings and unions, their connection types, real-world applications, and when contractors should choose one over the other.
Coupling vs. Union: Overview Comparison Table
Here’s a quick overview of pipe coupling vs. union, covering connection types, real-world applications, and how contractors choose the right fitting for plumbing, HVAC, and commercial systems.
| Feature | Pipe Coupling | Pipe Union |
| Primary Purpose | Permanently connect two pipes | Connect and disconnect pipes or equipment |
| Connection Type | Fixed | Removable |
| Maintenance Access | Low | High |
| Reusability | Not reusable | Reusable |
| Removal Method | Requires cutting pipe | Disconnects without cutting |
| Installation Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Long-Term Labor Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Pressure Handling | Excellent for high pressure | Best for moderate pressure |
| Best Use Case | Permanent pipe runs | Equipment and service connections |
| Common Placement | Long pipeline sections | Pumps, valves, boilers, HVAC units |
What Is a Pipe Coupling?
A pipe coupling is a short fitting used to connect two pipes in a straight line, creating a permanent extension of the pipeline. Once installed, removal typically requires cutting the pipe.
Core Characteristics
- Permanent connection
- High structural strength
- Leak-resistant under pressure
- Cost-effective
- Designed for long-term, fixed systems
Common Materials
- Galvanized pipe fittings carbon steel
- Stainless steel
- Black carbon steel
- PVC pipe couplings
- CPVC
- PEX-compatible couplings
Typical Connection Methods
- Threaded couplings use internal or external threads to join pipes, creating a strong, leak-resistant connection without welding socket. This method is common for smaller-diameter pipes and systems that do not require frequent disassembly. Threaded couplings are widely used in plumbing, residential HVAC, and smaller industrial applications where a secure, permanent connection is needed.
- Butt-welded couplings are installed by welding the ends of the pipe directly to the coupling, forming a continuous, high-strength joint. This connection method is ideal for high-pressure systems, industrial pipe fittings, and HVAC applications where durability and long-term integrity are critical. Once installed, butt-welded couplings are permanent and are not intended for regular removal or maintenance.
- Socket-weld couplings involve inserting a pipe into a recessed socket and welding around the joint, similar to socket-weld fittings unions. This method provides additional structural strength while maintaining precise alignment between pipe sections. Socket couplings are often used in mechanical, industrial, and high-pressure systems where alignment and pressure resistance are essential.
Typical Applications
- Water supply and drain systems
- Commercial plumbing distribution
- Structural mechanical piping works
- HVAC piping runs
- Agricultural and industrial pipelines
- PEX trunk-and-branch layouts
Contractor insight: Couplings are ideal where service access is not required, and long-term permanence is the priority.
What Is a Pipe Union?
A pipe union is a serviceable connection fitting that allows pipes or equipment to be disconnected without cutting or rotating the pipe. It consists of three parts: two pipe ends and a central nut that joins them.
Core Characteristics
- Removable connection
- Maintenance-friendly design
- Reusable fitting
- Ideal for equipment access points
- Reduces future labor costs
Common Materials
- Carbon steel
- Stainless steel
- Alloy steel
- Brass
- PVC
- PE
Connection Types
- Threaded unions use direct screw-in connections, making them quick and easy to install or remove without disturbing the rest of the piping system. This type is ideal for systems that require frequent maintenance, inspections, or equipment replacement, such as pumps, valves, and HVAC components. The threaded fitting design ensures a secure seal while allowing pipes to remain stationary during disassembly, which is especially useful in tight or hard-to-reach spaces.
- Socket-weld unions involve inserting a pipe into a recessed socket and welding it in place. This method provides a strong, durable connection capable of handling higher pressure ratings while still allowing controlled disassembly at the union joint. Socket welding union fittings are commonly used in industrial and commercial piping systems where structural integrity and long-term reliability are critical, but occasional maintenance or replacement may still be required.
Typical Applications
- Boilers and hydronic heating systems
- Pumps and circulators
- HVAC condensers and chillers
- Control valves and backflow preventers
- Water heaters and filtration systems
- Mechanical rooms and service corridors
Contractor insight: Unions are service pipe fittings. Their value is in access, not permanence.
Coupling vs. Union: What's the Difference?
- Coupling: Connects pipe-to-pipe permanently, designed for strength and pressure resistance, requires cutting for removal, best for fixed infrastructure.
- Union: Plumbing union fittings connect and disconnect components, designed for serviceability, allowing disassembly without rotating pipes, best for equipment pipe connections.
When to Use Each Fitting
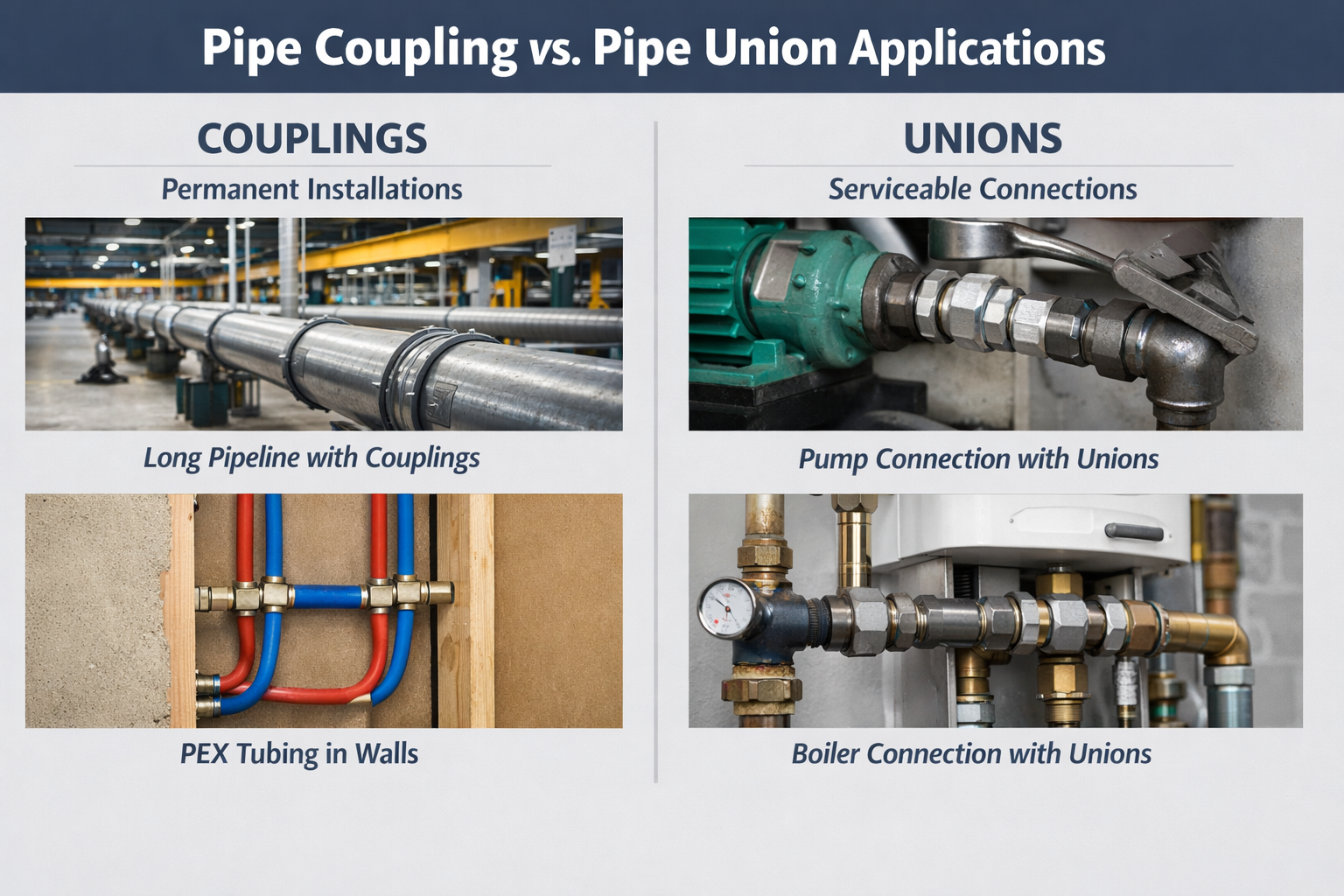
Coupling: Use when extending permanent pipelines, running PEX, copper, or steel through walls and slabs, building fixed HVAC networks, prioritizing cost over service access, or creating long structural pipe runs.
Union: Use when connecting pumps, boilers, or HVAC equipment, installing serviceable valves and meters, building mechanical rooms, planning for future maintenance, reducing downtime, or designing systems that require easy access.
Design Considerations: Pressure and Durability
- Couplings provide higher structural integrity in high-pressure and vibration-prone systems
- Unions provide maintenance access, not structural reinforcement
- In large-diameter systems, flange union often replace unions
- Proper placement matters more than fitting type
Standards, Codes, and Compliance
Couplings and unions are part of broader piping and mechanical codes. Contractors should follow guidance from IPC / ICC and other guides to ensure safe, maintainable, and reliable piping systems. Proper selection involves using materials rated for pressure and temperature, following approved installation practices, plumbing regulations, and providing serviceable access. For high-quality, code-compliant fittings, visit 24hr Supply.
Are You Ready for an Upgrade? Find the Right Fit
Quick access to emergency plumbing supplies and trade-grade fittings keeps crews moving and reduces downtime. A reliable 24 hour plumbing supply ensures teams can work efficiently and meet job timelines.
For example, a contractor retrofitting a commercial building initially used couplings on pump and valve connections to save material costs. Within a year, routine maintenance required cutting pipe, rethreading, and pressure testing. After switching to unions sourced from 24hr Supply, future service work was completed in hours instead of days, cutting labor costs and minimizing tenant disruption.
Explore different types of couplings and unions today at 24hr Supply and ensure your systems are built for performance and easy maintenance.
Recent Posts
-
What Causes Pipe Corrosion?
Pipe corrosion occurs when metal reacts with water, oxygen, and minerals over time. Factors that spe …Feb 2nd 2026 -
Commercial vs. Residential Plumbing: 15 Key Differences You Need to Know
Plumbing might seem straightforward at first glance, but residential and commercial systems are fund …Feb 2nd 2026 -
What Is a Circulator Pump and How Does It Work?
Water needs to keep moving efficiently in plumbing and HVAC systems, and that’s where a circulator p …Feb 2nd 2026